In nature, asexual females lay an average of 2.3 batches of eggs each season. If a female is housed alone, she lays only about 0.9 batches. If housed with a female whose hormonal state leads to male behavior, she lays 2.6 batches during the season. (Roughgarden 130)
New Mexico’s Environthon reports:
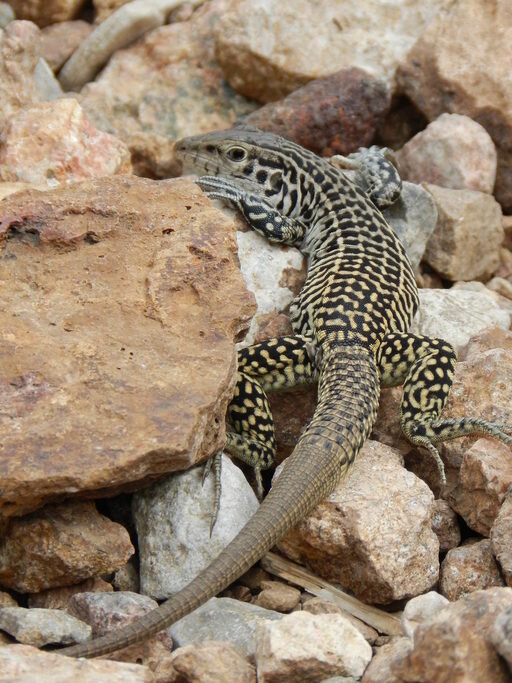
“The New Mexico Whiptail, as well as several other all-female species of whiptail lizard, does reproduce, and all of its offspring are female. Moreover, it reproduces by parthenogenesis -- its eggs require no fertilization, and its offspring are exact and complete genetic duplicates of the mother. Scientists understand only partially how this reproductive mode developed, and it raises many questions. One of the most intriguing is how this cloning affects the lizard's ability to adapt to environmental changes. Since there is no genetic variation except that which occurs through mutation, the New Mexico Whiptail cannot evolve as other species do.”
National Geographic Magazine (Nov 2016 issue) reports on the Baumann team’s research:
“The lizards are all female and parthenogenetic, meaning their eggs develop into embryos without fertilization. But before the eggs form, Baumann’s team discovered, the females’ cells gain twice the usual number of chromosomes—so the eggs get a full chromosome count and genetic variety and breadth (known as heterozygosity) rivaling that of a sexually reproducing lizard.
Why does this occur?
Because long ago, Baumann says, lizards of the genus Aspidoscelis had “a hybridization event”—that is, females of one species broke form and mated with males of another species. Those outlier liaisons gave whiptails robust heterozygosity, which has been preserved by the identical replication—essentially, cloning—that occurs in asexual reproduction. It’s a genetic-diversity advantage that today’s females still enjoy and propagate.”
Crews, D. (1987) Courtship in Unisexual Lizards: A Model for Brain Evolution. Scientific American Vol. 257, No. 6 (December 1987), pp. 116-121. writes:
“The females produce by parthenogenesis, that is, reproduction without fertilization, and therefore copulation between its members is not directly related to the production of offspring. Nevertheless, the females in this species actively engage in courtship rituals that are virtually identical with those observed between male and female whiptail lizards.”
Book Citations: Roughgarden, J. (2013) Evolution’s Rainbow: Diversity, Gender, and Sexuality in Nature and People. University of California Press, Berkeley. pp. 129-131.
Related Citations
D. Crews and K. Fitzgerald, 1980, "Sexual" behavior in parthenogenetic lizards (Cnemidophorus), Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 77:499-502
D. Crews, 1987, Courtship in unisexual lizards: A model for brain evolution, Scientific American 257 (6): 116-21.
L. Young and D. Crews, 1995, Comparative neuroendocrinology of steroid gene expression and regulation: Relationship to physiology and behavior, Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 6: 317-23.
D. Crews, M. Grassman, and J. Lindzey, 1986, Behavioral facilitation of reproduction in sexual and unisexual whiptail lizards, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 83:9547-50.
C. Cole and C. Townsend, 1983, Sexual behaviour in unisexual lizards, Anim. Behav. 31:724-28.
D. Crews and L. Young, 1991, Pseudocopulation in nature in a unisexual whiptail lizard, Anim. Behav. 42:512-14.
B. Leuck, 1982, Comparative burrow use and activity patterns of parthenogenetic and bisexual whiptail lizards (Cnemidophorus: Teiidae), Copeia 416-25.
B. Leuck, 1985, Comparative social behavior of bisexual and unisexual whiptail lizards (Cnemidophorus), J. Herpetology 19:492-506.
Y. Werner, 1980, Apparent homosexual behavior in an all-female population of a lizard, Lepidodactylus lugubris, and its probable interpretation, Tierpsychol. 52:144-50.
M.J. McCoid and R.A. Hensley, 1991, Pseudocopulation in Lepidodactylus lugubris, Herpetological Review 22:8-9.
Dias, B. G., & Crews, D. (2006). Serotonergic modulation of male-like pseudocopulatory behavior in the parthenogenetic whiptail lizard, Cnemidophorus uniparens. Hormones and behavior, 50(3), 401–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2006.05.001
Paulissen, M., & Walker, J. (1989). Pseudocopulation in the Parthenogenetic Whiptail Lizard Cnemidophorus laredoensis (Teiidae). The Southwestern Naturalist, 34(2), 296-298. doi:10.2307/3671747